Mathematics Formula – Algebra & Mensuration
Algebra
- (a+b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
- (a – b)2 = a2 – 2ab + b2
- a2 + b2 = (a+b)2 – 2ab = (a – b)2 + 2ab
- (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2ac + 2bc
- (a – b – c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 – 2ab – 2ac + 2bc
- (a – b – c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 – 2ab – 2ac + 2bc
- a2 – b2 = (a – b)(a + b)
- (a + b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3ab(a + b)
- (a – b)3 = a3 – b3 – 3ab(a – b)
- a3 – b3 = (a – b)(a2 + ab + b2)
- a3 + b3 = (a + b)(a2 – ab + b2)
- an – bn = (a – b)(an-1 + an-2b+…+ bn-2a + bn-1) | n is a natural number.
- aman = am+n
- (ab)m = ambm
- (am)n = amn
- am/ an = am-n
- (a/b)n = an/ bn
- a0 = 1
- a-n = 1/ an
- logamn = logam + logan
- loga(m/n) = logam – logan
- logamn = n.logam
- logba = logka / logkb
- logba = 1/ logab
- (x+a)(x+b) = x2 + (a+b)x + ab
Progression(Series)
1-Arithmetic Progression(AP)
a, a+d, a+2d, a+3d, …, …, …,l(last term)
a-First Term, d-Common Difference, l-Last Term
- nth Term = Tn = a + (n-1)d
- Sum of n Terms = Sn = n/2[2a + (n-1)d] = n/2[first term + last term]
2-Geometric Progression(GP)
a, ar, ar2, ar3, ar4, ….
a-First Term, r-Common Ratio
- nth Term = Tn = arn-1
- Sum of n Terms = Sn = a(1-rn) / (1-r)
- Sum of ∞ Terms = S∞ = a / (1-r)
3-Harmonic Progression(HP)
a1, a2, a3, a4, …, …. are said to be in Harmonic Progression(HP) if and only if 1/a1, 1/a12, 1/a3, 1/a4, … are in Arithmetic Progession(AP).
VBODMAS Rule
V- Vinculumor or Bar
B- Bracket
O- Of
D- Division
M- Multiplication
A- Addition
S- Subtraction
Average
- Average of First n Natural Numbers = (n+1)/2
- Average of First n Even Numbers = n+1
- Average of First n odd Numbers = n
- Average of Consecutive Numbers = (First No. + Last No.) / 2
- Average of squares of First n Natural Numbers = (n+1)(2n+1) / 6
- Average of Cubes of First n Natural Numbers = n(n+1)2 / 4
Percentage
y% of x = x * y/100
- 5% of a number = number/20
- 10% of a number = number/10
- 20% of a number = number/5
- 25% of a number = number/4
- 50% of a number = number/2
Profit and Loss
- Profit = Selling Price – Cost Price
- Loss = Cost Price – Selling Price
- Profit% = (Profit/Cost Price) * 100
- Loss% = (Loss/Cost Price) * 100
- Selleng Price = (100 + Profit%) * Cost Price / 100
- Selleng Price = (100 – Loss%) * Cost Price / 100
- Cost Price = 100 * Selling Price / (100 + Profit%)
- Cost Price = 100 * Selling Price / (100 – Loss%)
Discount
- Discount = Marked Price – Selling Price
- Discount% = (Discount/Marked Price) * 100
- Selling Price = Marked Price – Discount
- Selling Price = Marked Price * (1 – r/100)
Simple Interest
- Simple Interest = (Principal * Rate * Time)/100
- Total Amount = Principal + Simple Interest = P + SI = P + PRT/100
= P(1 + RT/100) - Principal = (Amount * 100) / (100 + RT)
- Simple Interest = (Amount * Rate * Time) / (100 + RT)
P = Principal Amount, A = Total Amount, R = Rate of Interest (Annual)
T = Time
Compound Interest
- In Compound Interest the amount at the end of each year becomes the principal for the next year.
- Total Amount = P(1 + R/100)T
- P = Principal Amount, R = Rate of Interest(Annual), T = Time
Factorial
- n! = n(n-1)(n-2)(n-3)……*1
Combination
- Number of Combinations of n different things when r things are taken into consideration. (Order is not important)
nCr = n! / r!(n-r)!
Permutation
- The number of Permutation of n different things taken r at a time
nPr = n! / (n-r)!
Probability
Probability of happening of an event = (Number of Favourable events) / (Total Number of possible outcomes)
Mensuration
Triangle
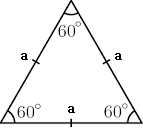
Equilateral Triangle:
- All three sides of the Equilateral Triangle are equal.
- Each angle of the Equilateral Triangle is 60o
-
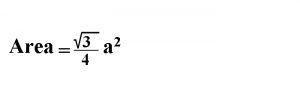
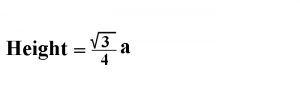
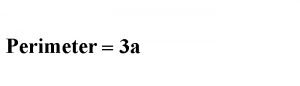
Isosceles Triangle:
- 2 Sides and 2 Angles are equal.
- Altitude drawn on nonequal side bisects it.
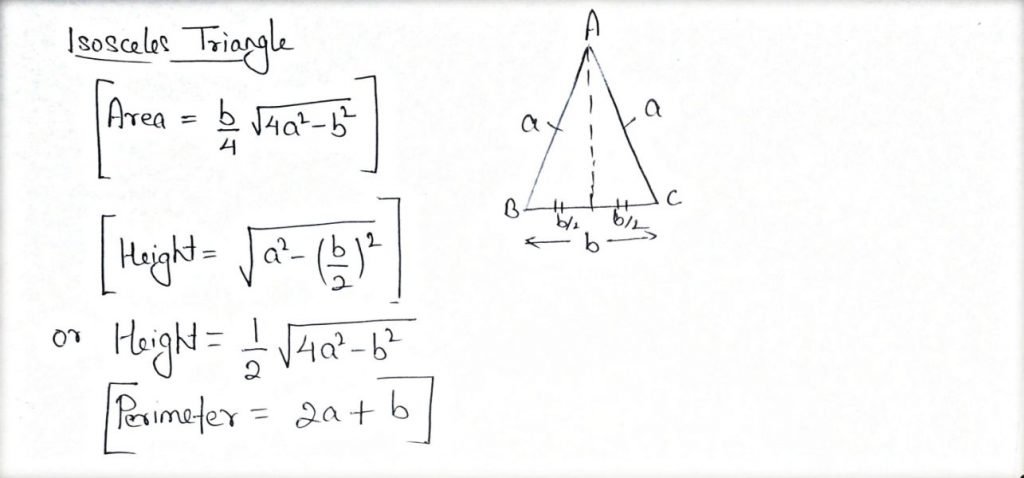
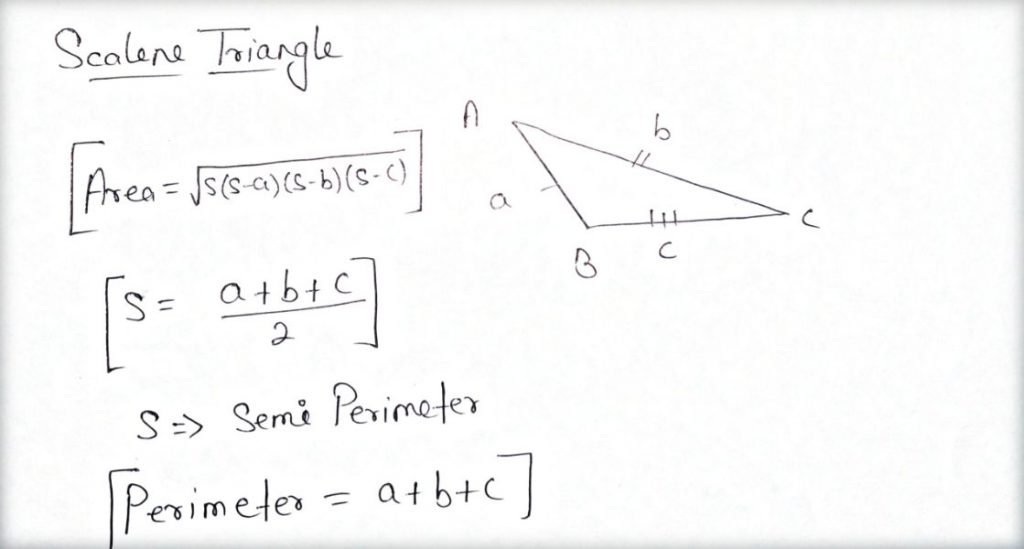
Scalene Triangle:
- All the 3 sides are unequal.
Right Angle Triangle:
- One of the angles is 90o

Isosceles Right Angle Triangle:
- One of the angle is 90o
- 2 Sides are equal.

Properties of Triangle:
- Sum of any 2 sides of any triangle is greater than the third side.
- For a constant Perimeter, Equilateral Triangle will have the maximum area.
- Median: The line joining the midpoint of any side of triangle to the opposite vertex.
- The median of a triangle divides the triangle into triangle of two equal area.
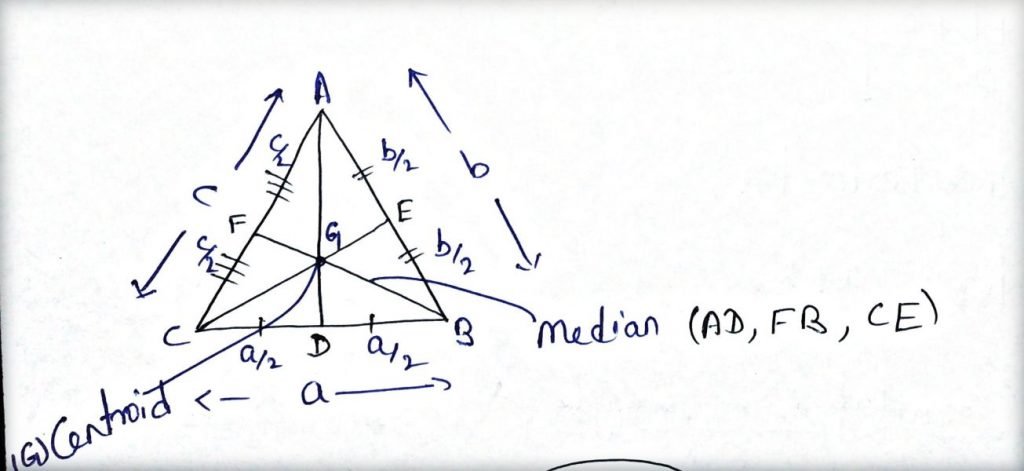
Inner Circle and Circumcircle of Equilateral Triangle:
- 2 Let the side of equilateral triangle is a

Quadrilateral:
- Figure enclosed by 4 sides.
- Sum of all the 4 angles = 360o
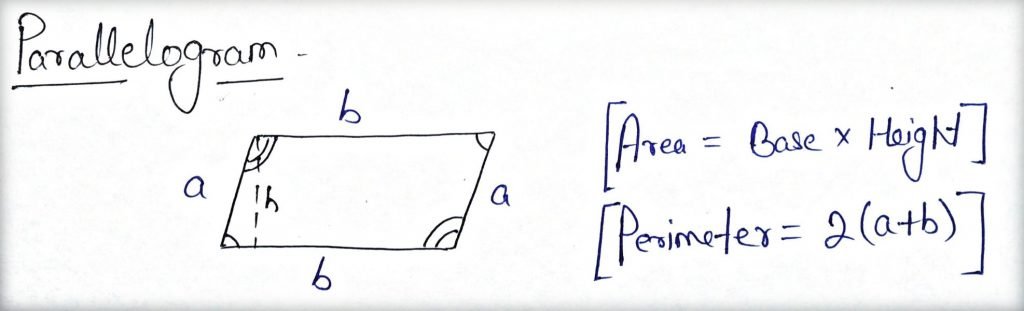
Parallelogram:
- The opposite sides are parallel.
- Diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
- The diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into 2 triangles of equal area.
- The opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal.
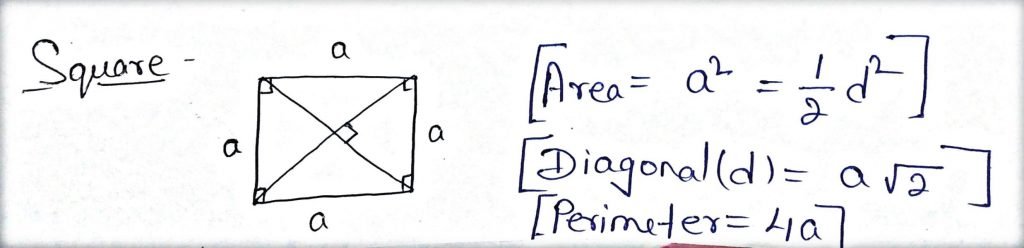
Square:
- It is a parallelogram that has all 4 sides equal and each angle is 90o
- The diagonal of a square are equal & bisect each other at 90o
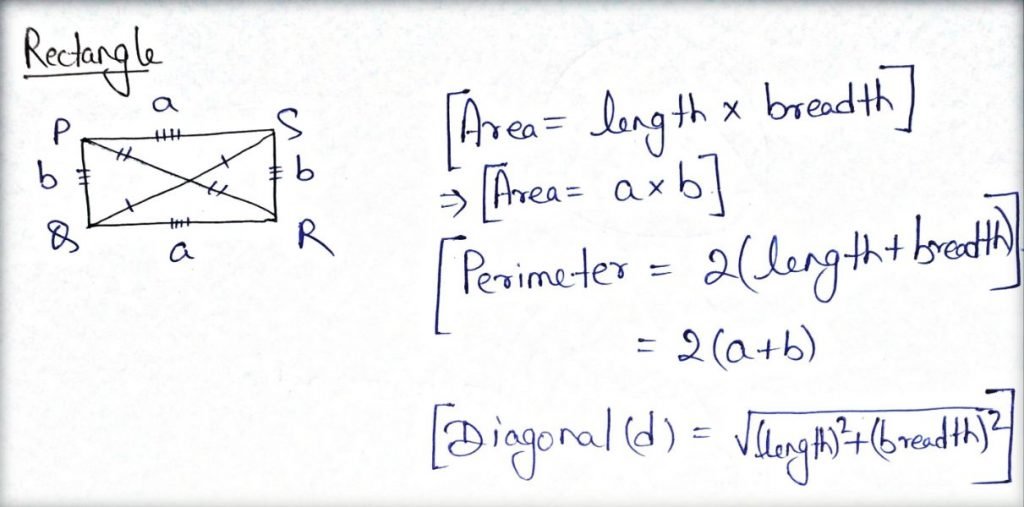
Rectangle:
- It is a parallelogram with equal opposite sides and each angle is 90o
- The diagonals of a rectangle are equal.
- The diagonal of a rectangle bisect each other.
Trapezium:
- It is a quadrilateral with one pair of opposite sides parallel.

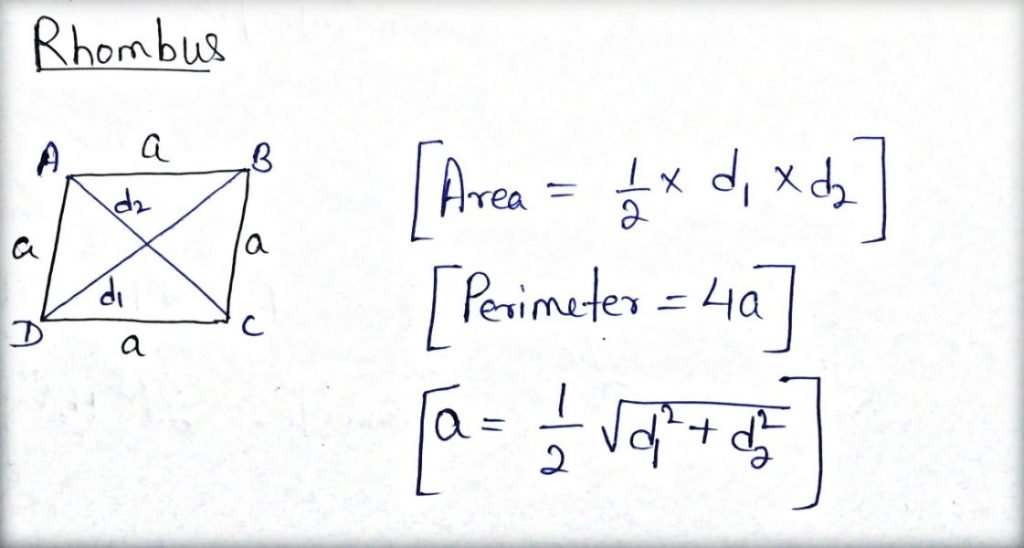
Rhombus:
- It is a parallelogram with all 4 sides equal.
- The opposite angles of a rhombus are equal but not 90o .
- It has unequal diagonal but they bisect each other at 90o .
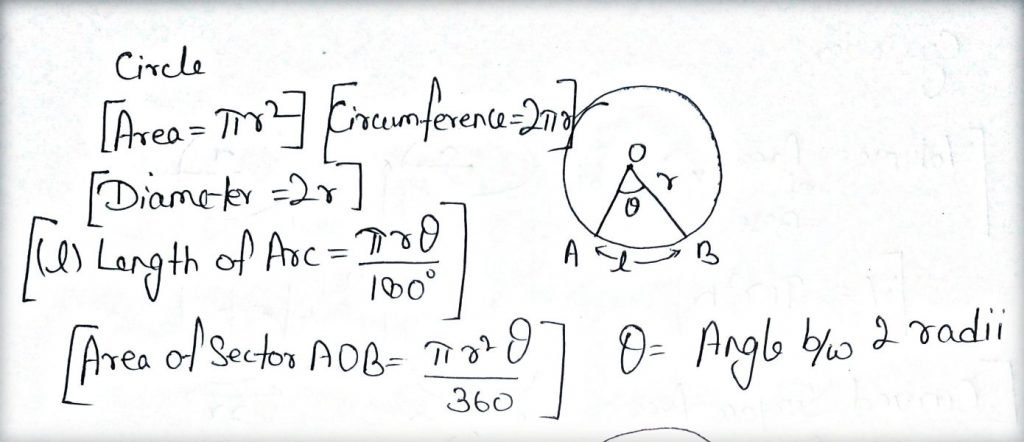
Circle:
- Let r be the radius of the circle.
- l is the length of Arc.
Semi Circle:
- A circle when separated into 2 parts along its diameter.

Circular Ring:

Volume Surface & Area
Cube
- A solid body having 6 equal faces with equal length, breadth and height is called cube.
- Each face of the cube is a square.
- Let a be the side of the cube.

Cuboid:
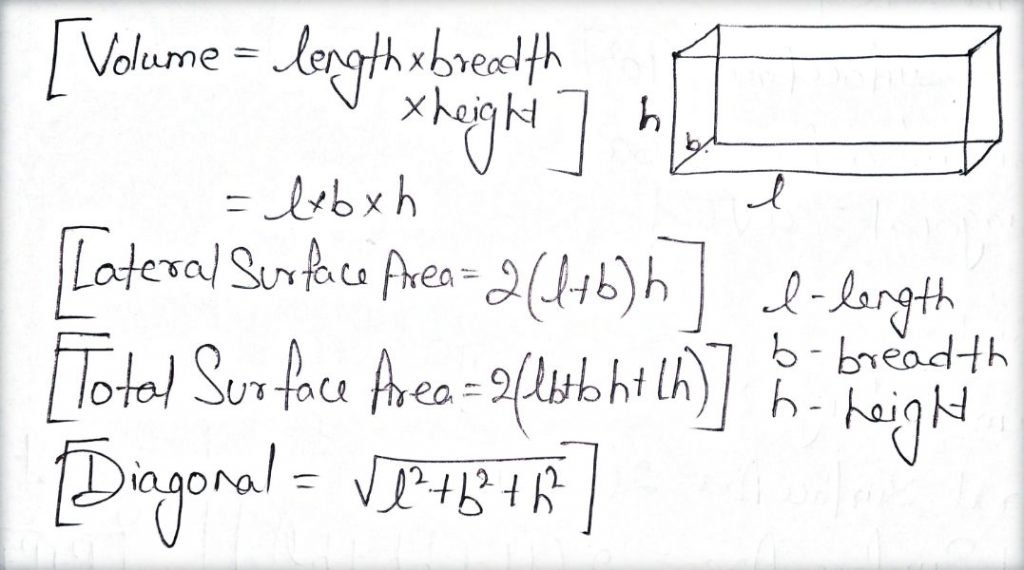
Cylinder:

Hollow Cylinder:

Cone:

Sphere:

Hollow Sphere or Spherical Shell:

Hemisphere:



 Users Today : 508
Users Today : 508 Total views : 472989
Total views : 472989