What are Nouns?
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns can be concrete, like “dog” or “book”, which refer to physical objects that you can see and touch. They can also be abstract, like “love” or “happiness”, which represent concepts that can’t be touched or seen.
Nouns can be singular or plural. A singular noun refers to one person, place, thing, or idea, while a plural noun refers to more than one. For example, “cat” is a singular noun, while “cats” is the plural form.
Nouns can also be proper or common. Proper nouns refer to specific people, places, or things, and are capitalized. Examples include “John”, “Paris”, and “Mount Everest”. Common nouns, refer to general people, places, or things, and are not capitalized unless they start a sentence. Examples of common nouns include “man”, “city”, and “mountain”.
Definition and Examples of Different Types of Nouns
Nouns can be classified in several ways based on their meaning and grammatical features. Here are some common ways to classify nouns in English:
Common and Proper Nouns
Common Nouns
A common noun is a type of noun that refers to a general or non-specific person, place, thing, or idea. Common nouns are not capitalized unless they begin a sentence or are part of a title. They can refer to everyday objects or concepts that do not require specific identification. For example, “city,” “dog,” and “book” are all common nouns. Common nouns can be singular/plural, and they can be used as subjects, objects, or indirect objects in a sentence.
Proper Nouns
These are nouns that refer to a specific person, place, or thing, and are always capitalized. Examples include John, New York City, The Eiffel Tower, and The Beatles.
Proper nouns are often contrasted with common nouns. Proper nouns refer to a specific person, place, or thing and are always capitalized. For example, “New York City” is a proper noun, while “city” is a common noun. Understanding the difference between common and proper nouns is important for grammatical accuracy in writing and speaking.
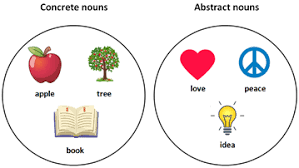
Concrete and Abstract Nouns
Concrete Nouns
It refers to a physical, tangible, or material object that can be seen, heard, touched, smelled, or tasted. Concrete nouns can be perceived through the five senses. They include things like people, animals, plants, places, and things. Examples of concrete nouns include “dog,” “cat,” “tree,” “house,” and “car.”
Abstract Nouns
It refers to an intangible concept, idea, quality, or state, rather than a physical, tangible object. Abstract nouns cannot be perceived through the five senses and are usually only experienced or understood through thought or emotion. Examples of abstract nouns include “love,” “happiness,” “justice,” “intelligence,” and “freedom.”
Abstract nouns are often the opposite of concrete nouns, which refer to physical, tangible objects that can be seen, touched, or heard. Abstract nouns can be challenging to define and understand because they are not tangible. But, they are important for expressing and exploring complex ideas and emotions.
Countable and Uncountable Nouns
Countable Nouns
These are nouns that can be counted or quantified. Examples include a book, dog, pencil, apple, cup.
Uncountable Nouns
These are nouns that cannot be counted or quantified. Examples include water, air, sugar, knowledge, and happiness.

Collective Nouns
A collective noun is a type of noun that refers to a group of people, animals, or things considered as a single entity. Collective nouns are used to describe a collection or group of individual items or entities, and they can be singular or plural. Examples of collective nouns include “family,” “herd,” “flock,” “team,” “committee,” and “audience.”
Collective nouns can be tricky because they can take either a singular or plural verb depending on the context. For example, “The team is practicing” uses a singular verb because the team is being treated as a single entity, while “The team are arguing with each other” uses a plural verb because the individuals within the team are being emphasized.
Some collective nouns are always plural, such as “scissors,” “pants,” and “glasses.” These nouns refer to items that come in pairs or multiples, and as such, they are treated as plural regardless of their context.

Compound Nouns
It is a type of noun, created by combining two/more words to form a new word with a specific meaning. They can be made up of two nouns, (adjective,noun), (verb , noun), ( preposition, noun) etc.
They can be written as separate words, hyphenated words, or a single word, depending on the context and the style guide being used. For example, “hot dog” is a compound noun that is written as two separate words. Where as “mother-in-law” is a compound noun that is hyphenated.
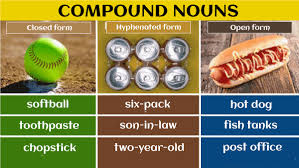
Compound nouns can refer to specific concepts or things that do not have a single-word equivalent. For example, “ice cream” is a compound noun that refers to a specific type of frozen dessert. While “football” is a compound noun that refers to a specific sport.
Understanding compound nouns is important for effective communication, as they can help to create more precise and specific language. By combining words to create new, unique concepts, allow for a more nuanced understanding of the world around us.
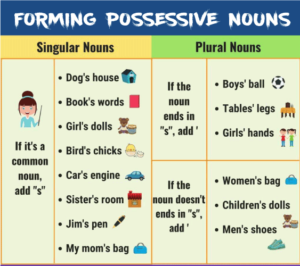
Possessive Nouns
A possessive noun is a type of noun that shows ownership or possession. They are usually formed by adding an apostrophe and an “s” (‘s) to the end of the noun. Or just an apostrophe (‘) to the end of plural nouns that already end in “s.” For example, “John’s book,” “the cat’s tail,” and “the students’ desks” are all possessive nouns.
They can be used to describe a relationship between two or more nouns, like “the company’s CEO” or “the government’s policies.” In these cases, the possessive noun shows that one noun is related to or belongs to the other noun.
It is important to use possessive nouns correctly in writing and speech, as they help to clarify ownership or possession. When using a singular noun, the apostrophe and “s” (‘s) are added to the end of the noun to form the possessive. When using a plural noun, the apostrophe is added after the “s” to form the possessive. However, there are some exceptions to this rule. So it’s important to consult a grammar guide if you’re not sure about the correct usage.
Verbal Nouns
Verbal nouns, also known as a gerund. They are formed from a verb by adding -ing to the base form of the verb. Verbal nouns function as nouns in a sentence and can be used as subjects, objects, or complements.
For example, in “Swimming is my favorite sport,” “swimming” is a verbal noun that functions as the subject. In “I enjoy hiking in the mountains,” “hiking” is a verbal noun that functions as the direct object of “enjoy.”
Verbal nouns can be confusing because they look like verbs, but function as nouns. They are often used to express activities or actions in a more general way. They can be modified by adjectives or adverbs, just like regular nouns.
Verbal nouns can also be used after prepositions, like “I am thinking about going to the store”. In this case, the verbal noun functions as the object of the preposition.
It is important to note that not all words that end in -ing are verbal nouns. Some are participles, which function as adjectives, while others are part of a continuous verb tense. This indicates an ongoing action. However, in the context of verbal nouns, -ing is used to create a noun that refers to the action or activity expressed by the verb.
What are Nouns? Definition and Examples: Conclusion
We have discussed ‘ What are Nouns? Definition and Examples in this article. Overall, nouns are an essential part of the language. They allow us to communicate about the world around us by giving names to people, places, and things. Understanding the different types of nouns can help to improve communication and clarity in writing and speech.
What are Nouns? Definition and Examples. FAQs?
1. What is a noun?
Ans. A noun is a word that is used to name a person, place, thing, or idea.
2. What are the different types of nouns?
Ans. The different types of nouns include:
Common nouns (e.g. cat, city, tree)
Proper nouns (e.g. Paris, John, McDonald’s)
Concrete nouns (e.g. table, phone, dog)
Abstract nouns (e.g. love, courage, sadness)
Collective nouns (e.g. team, flock, audience)
Compound nouns (e.g. swimming pool, ice cream, mother-in-law)
3. What is a common noun?
Ans. A common noun is a type of noun that refers to a general category of people, places, things, or ideas.
4. What is a proper noun?
Ans. A proper noun is a type of noun that refers to a specific, named individual, place, or thing.
5. What is a concrete noun?
Ans. A concrete noun is a type of noun that refers to a tangible, physical object that can be seen, heard, touched, tasted, or smelled.
6. What is an abstract noun?
Ans. An abstract noun is a type of noun that refers to an intangible concept or idea that cannot be seen, heard, touched, tasted, or smelled.
7. What is a collective noun?
Ans. A collective noun is a type of noun that refers to a group of people, animals, or things.
8. What is a compound noun?
Ans. A compound noun is a type of noun that is formed by combining two or more individual words to form a new word with a specific meaning.

